BBO 基准测试函数
在这个开源 Python 模块中,我们提供了一套在黑盒优化(BBO)/零阶优化/无梯度优化/无导数优化/全局优化/直接搜索/随机优化/元启发式算法/进化算法/群体智能社区中常用的**基准/测试函数**。
注意
在未来,我们计划添加一些来自各种**现实世界应用**的**具有挑战性**的 BBO 模型。由于这是一个*长期*开发项目,欢迎任何人为此做出任何开源贡献。
对于一套包含 23 个基准/测试函数,它们的**基本**形式、**平移/变换**形式、**旋转**形式以及**旋转-平移**形式都已编码并经过*充分测试*。通常,在 BBO 的**比较实验**中应使用它们的**旋转-平移**形式,以避免可能对某些搜索点(例如原点)或可分离性产生偏见。
编码正确性检查
关于所有基准测试函数的测试代码,请参阅以下公开链接获取详细信息(事实上,我们花费了大量时间来检查 Python 编码的正确性):
基本函数
这里我们介绍一些在优化文献中常见的基准测试函数的**基本**形式,如下所示:
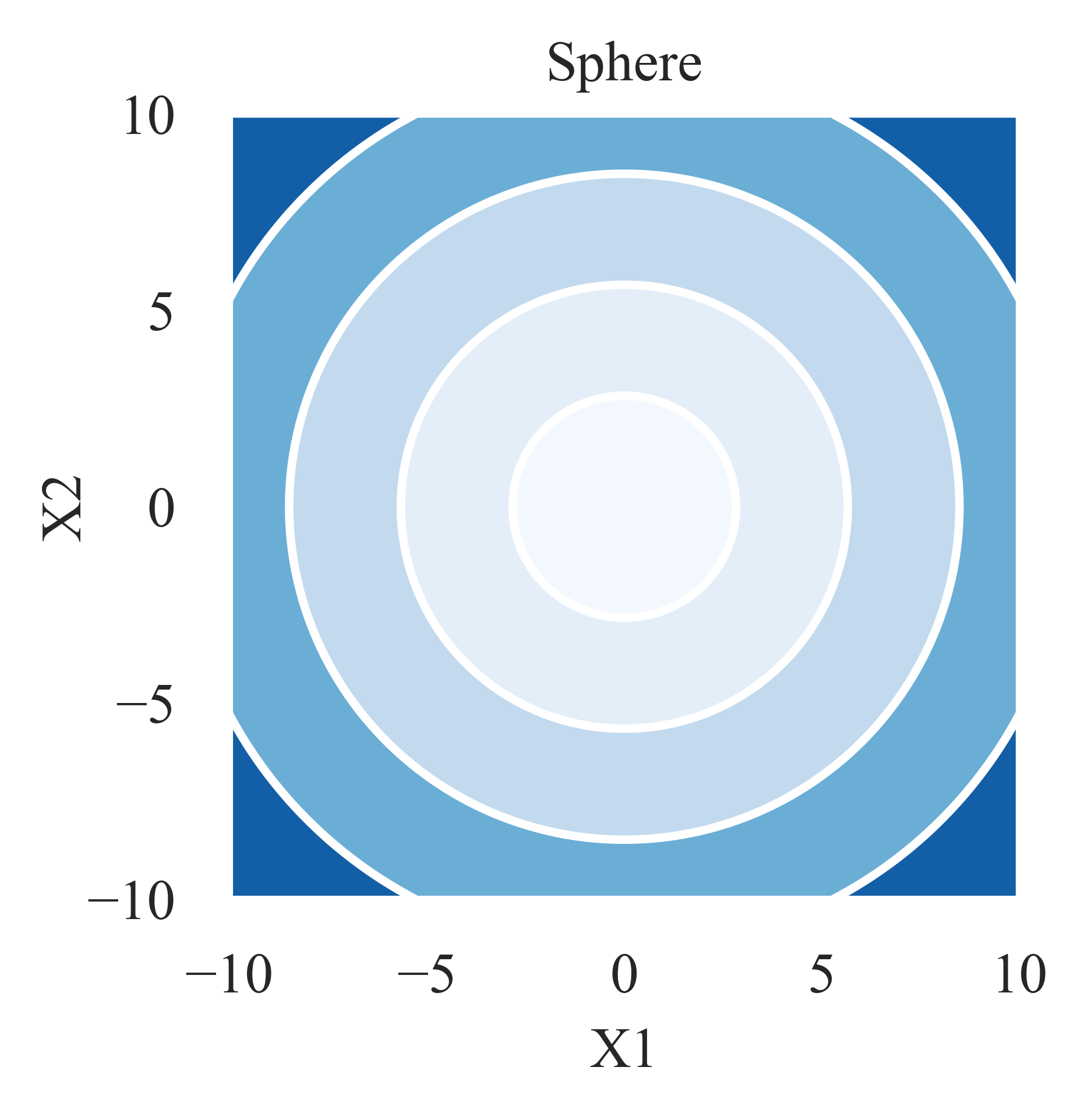
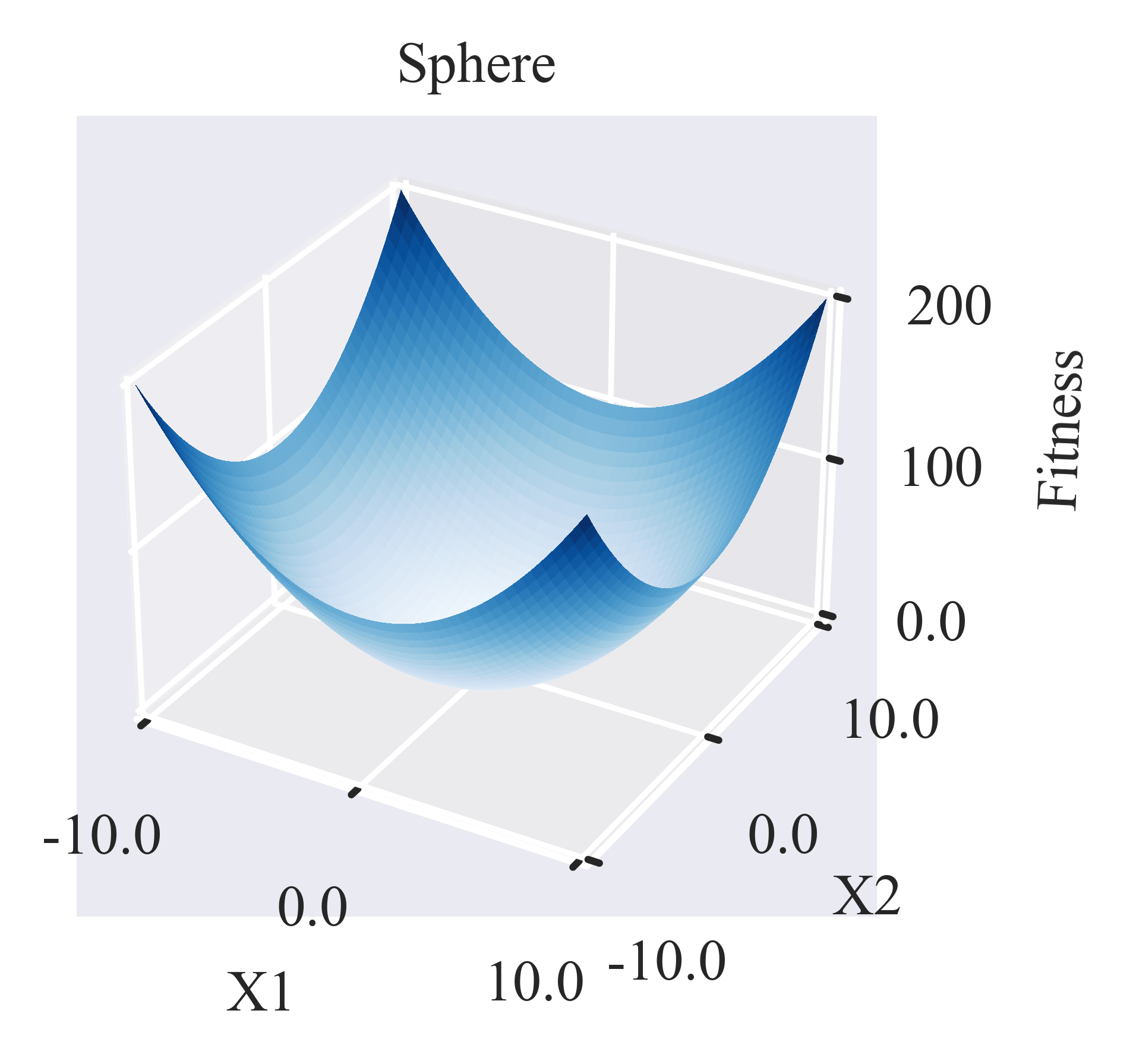
其 3D 曲面图生成脚本:https://github.com/Evolutionary-Intelligence/pypop/blob/main/tutorials/plotting/surface/plot_surface_for_sphere.py
参考文献(部分)
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
Zhou, Q. and Li, Y., 2003. Directed variation in evolution strategies. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 7(4), pp.356-366.
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.cigar(x)[源代码]
**Cigar** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
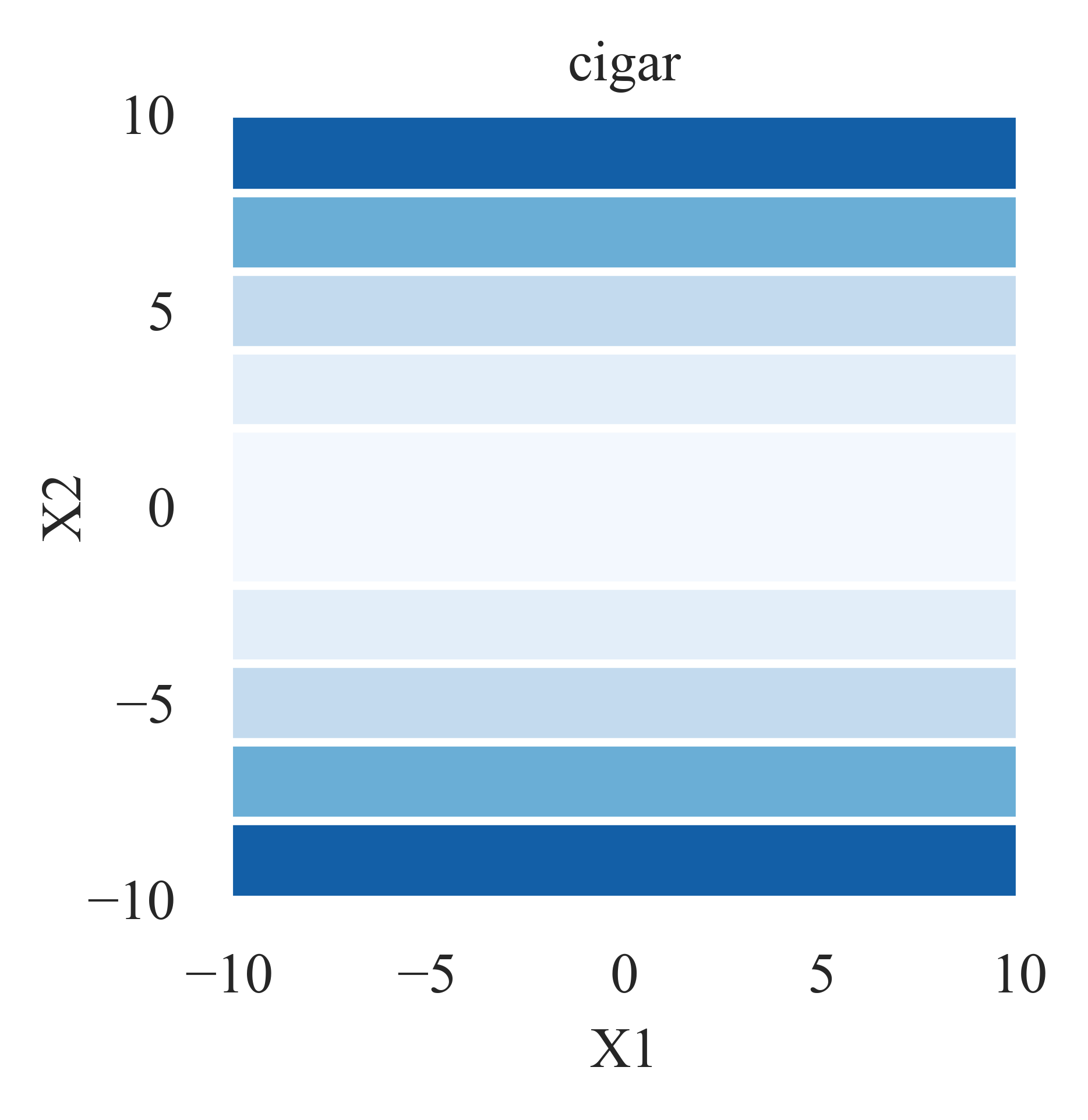
其 2D 景观图生成脚本:https://github.com/Evolutionary-Intelligence/pypop/blob/main/tutorials/plotting/landscape/plot_landscape_for_cigar.py
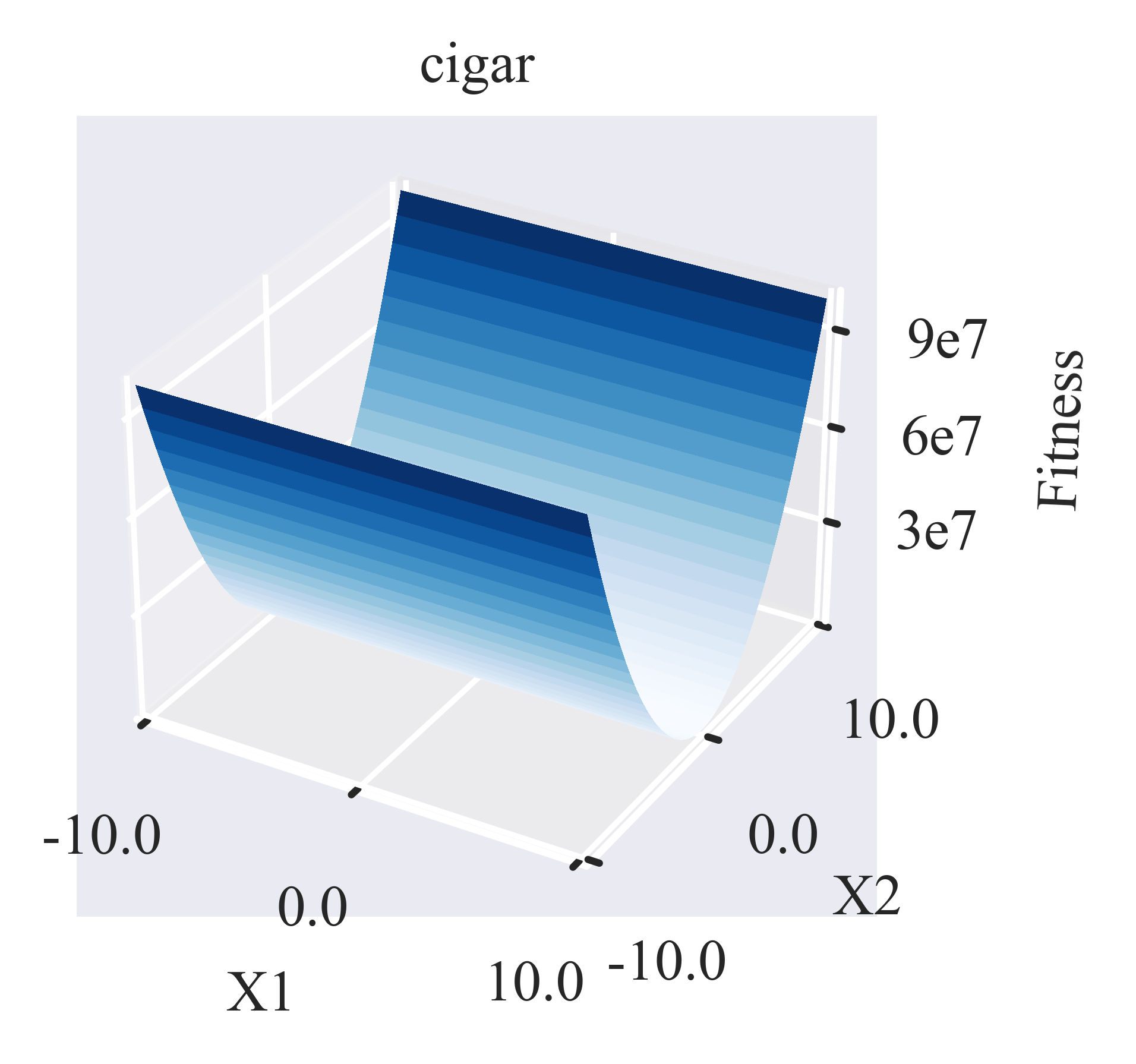
其 3D 曲面图生成脚本:https://github.com/Evolutionary-Intelligence/pypop/blob/main/tutorials/plotting/surface/plot_surface_for_cigar.py
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
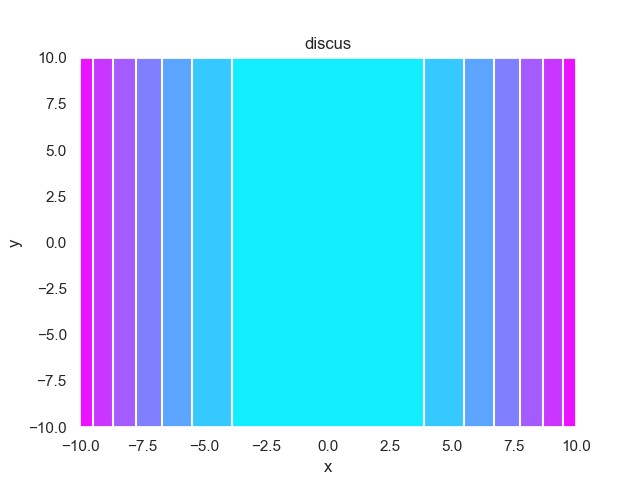
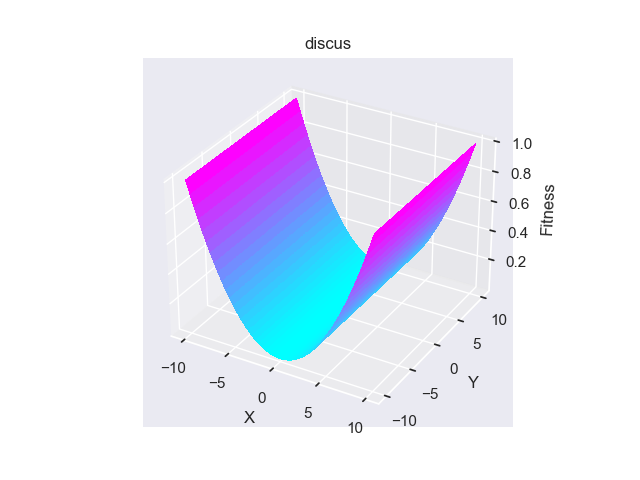
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.discus(x)[源代码]
**Discus**(也称为 **Tablet**)测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
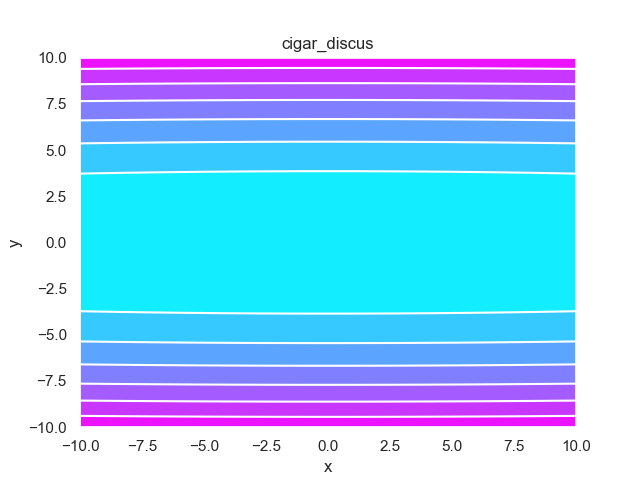
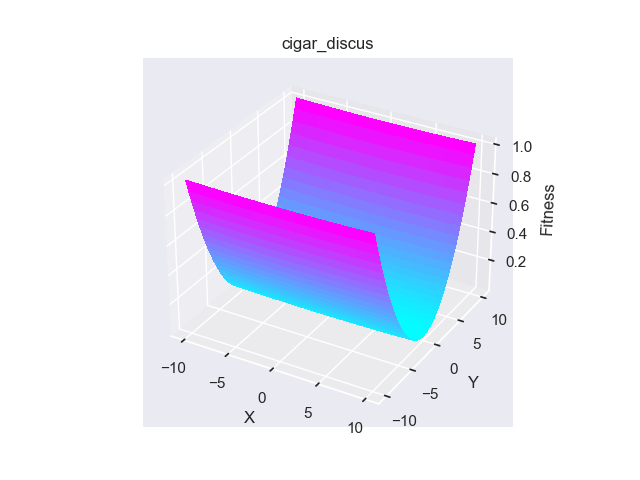
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.cigar_discus(x)[源代码]
**Cigar-Discus** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
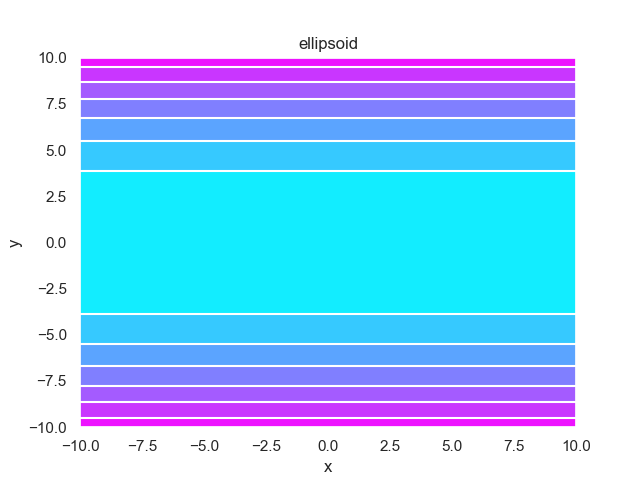
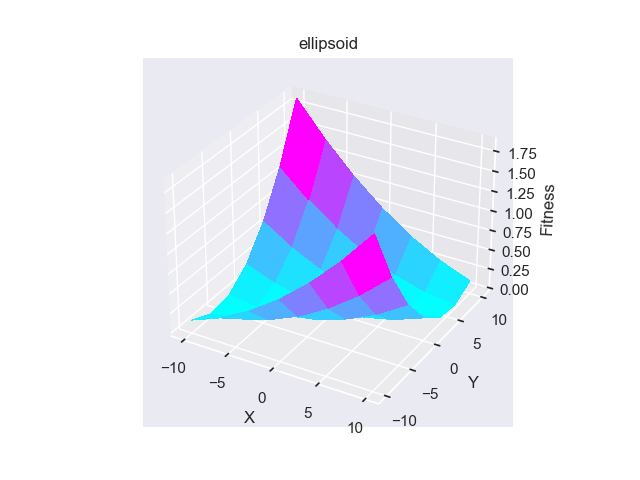
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.ellipsoid(x)[源代码]
**Ellipsoid** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
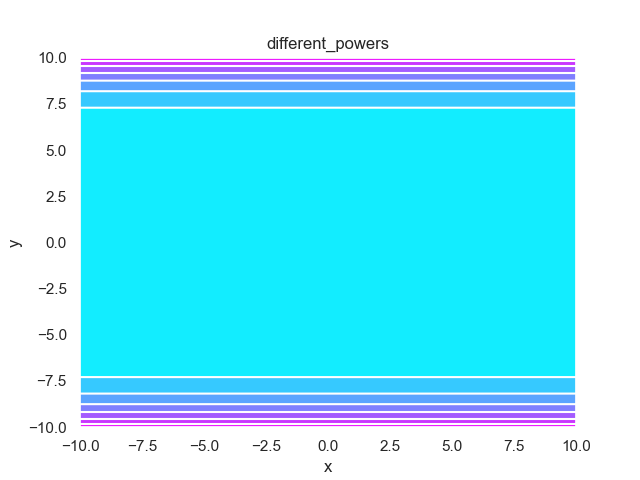
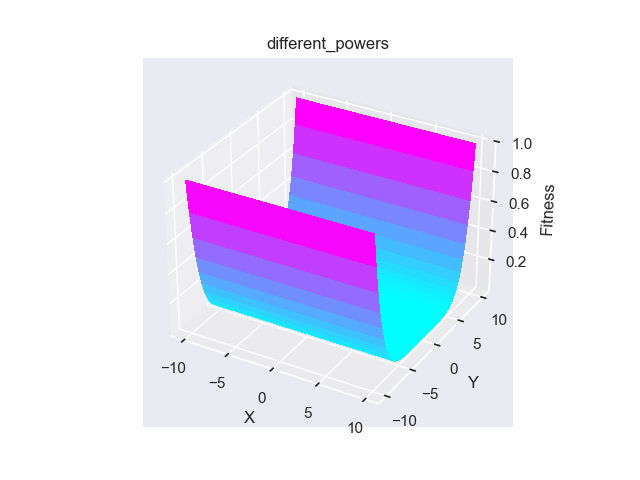
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.different_powers(x)[源代码]
**Different-Powers** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
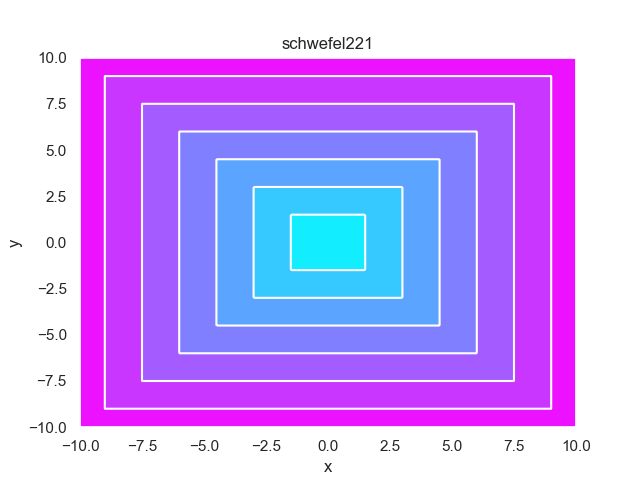
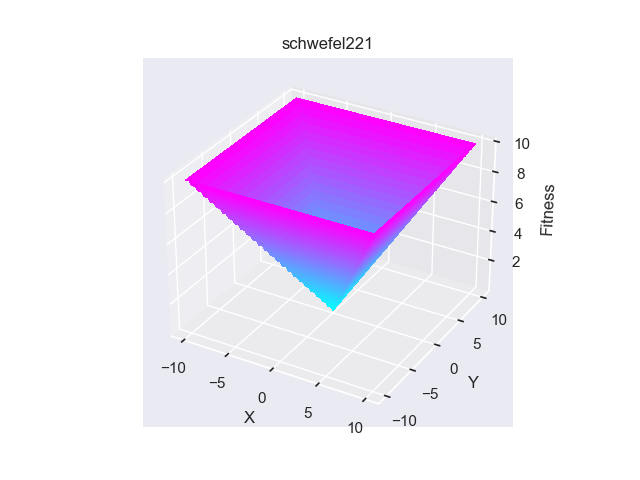
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel221(x)[源代码]
**Schwefel221** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
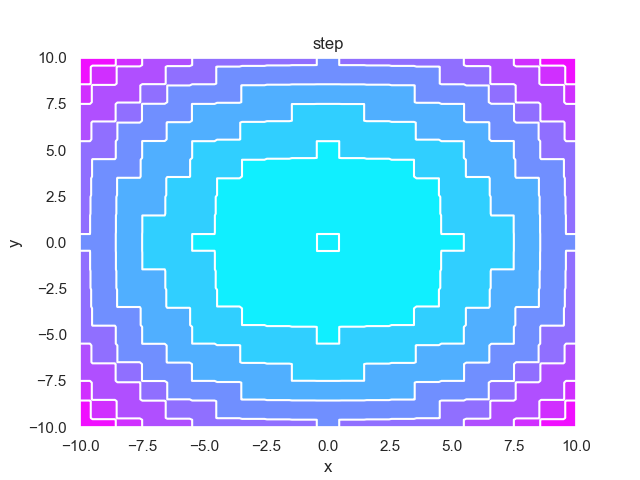
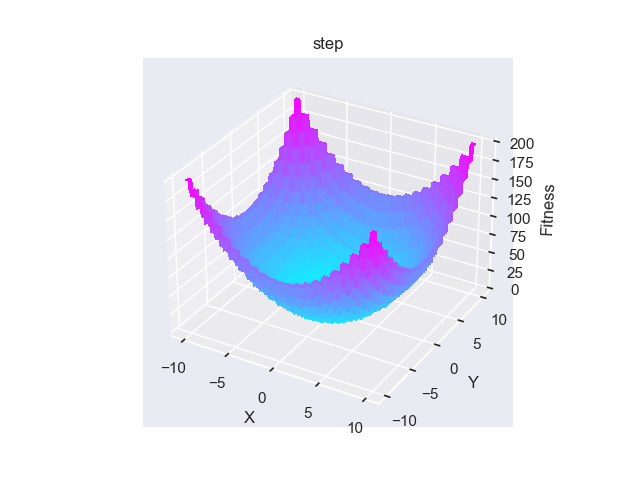
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.step(x)[源代码]
**Step** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
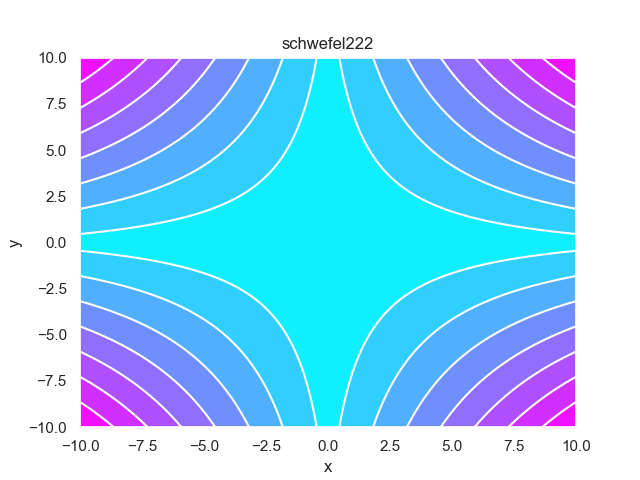
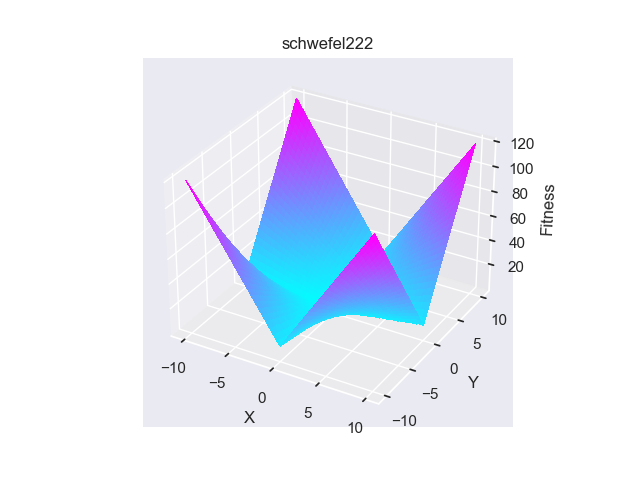
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel222(x)[源代码]
**Schwefel222** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
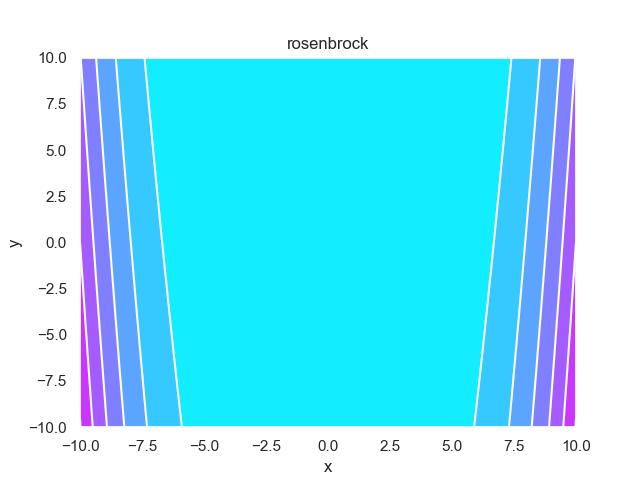
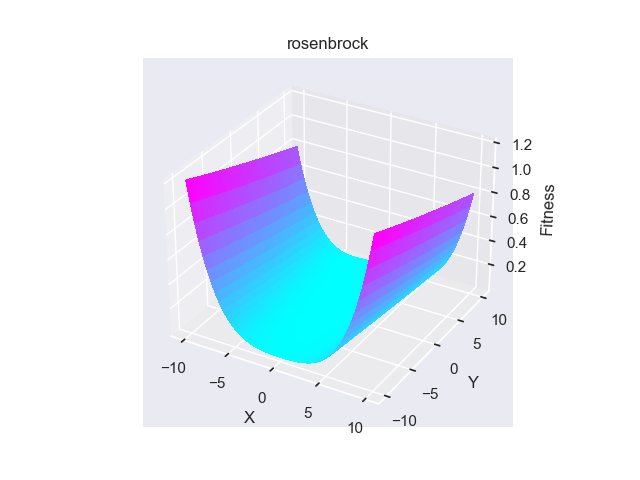
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.rosenbrock(x)[源代码]
**Rosenbrock** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Loshchilov, I., Glasmachers, T. and Beyer, H.G., 2018. Large scale black-box optimization by limited-memory matrix adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 23(2), pp.353-358.
Beyer, H.G. and Sendhoff, B., 2017. Simplify your covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 21(5), pp.746-759.
Jastrebski, G.A. and Arnold, D.V., 2006, July. Improving evolution strategies through active covariance matrix adaptation. In IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 2814-2821). IEEE.
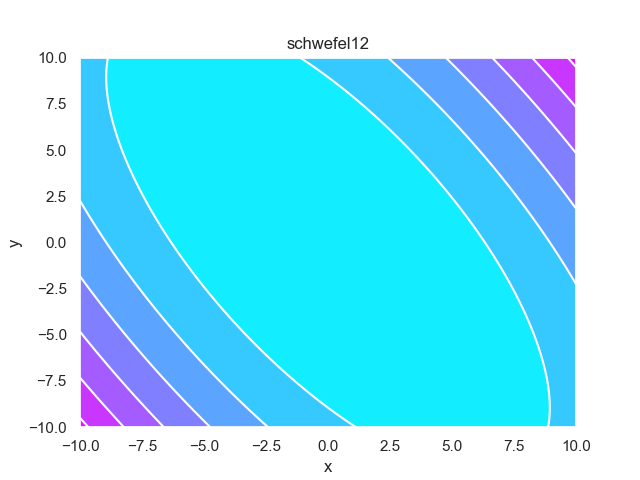
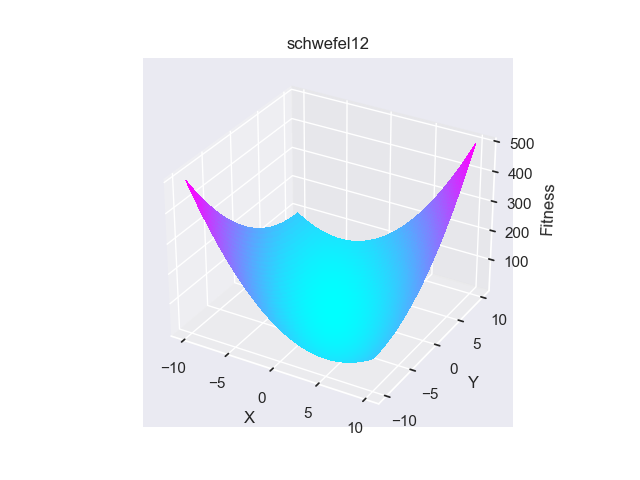
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schwefel12(x)[源代码]
**Schwefel12** 测试函数。
注意
其维度应 > 1。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
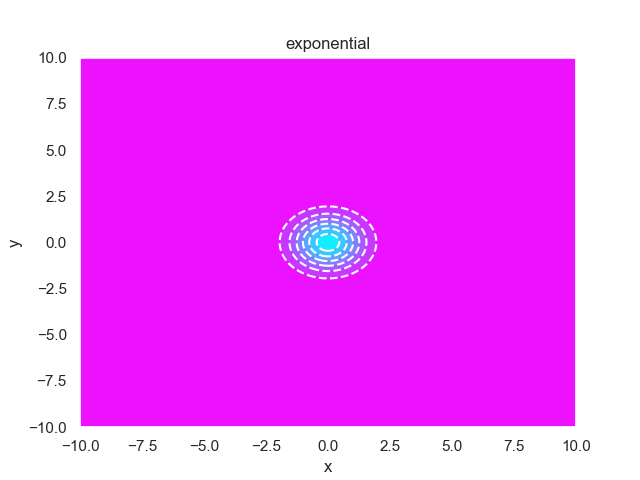
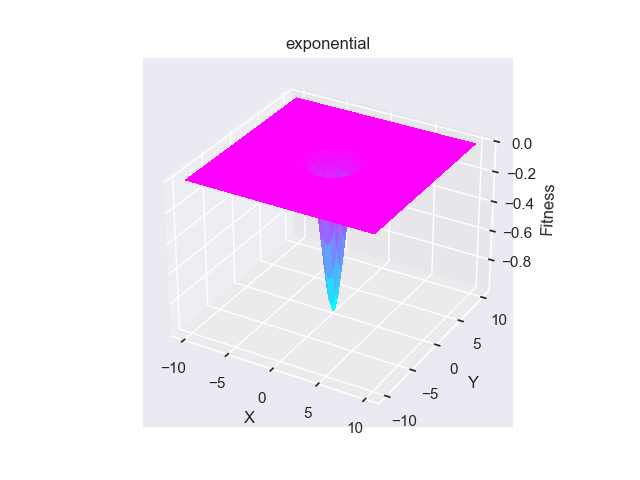
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.exponential(x)[源代码]
**Exponential** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.griewank(x)[源代码]
**Griewank** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float

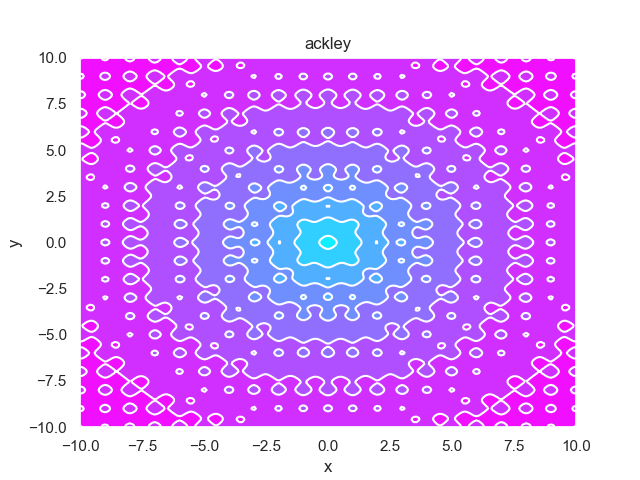
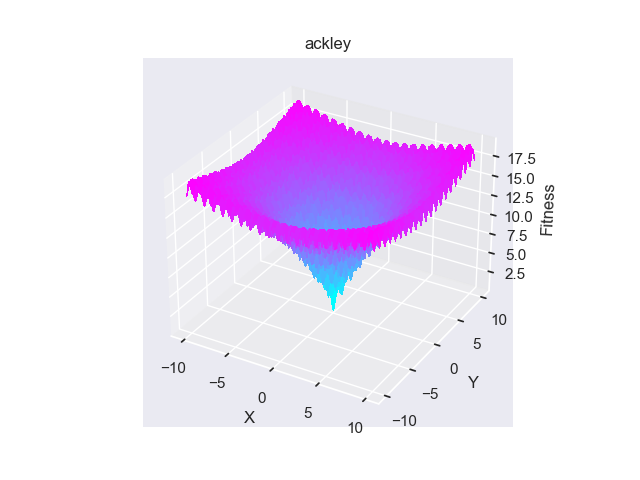
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.ackley(x)[源代码]
**Ackley** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
Bungert, L., Roith, T. and Wacker, P., 2024. Polarized consensus-based dynamics for optimization and sampling. Mathematical Programming, pp.1-31.
Carrillo, J.A., Choi, Y.P., Totzeck, C. and Tse, O., 2018. An analytical framework for consensus-based global optimization method. Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences, 28(06), pp.1037-1066.
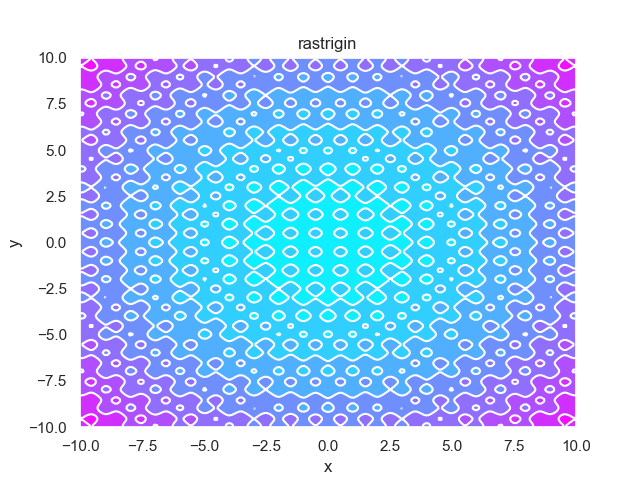
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.rastrigin(x)[源代码]
**Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
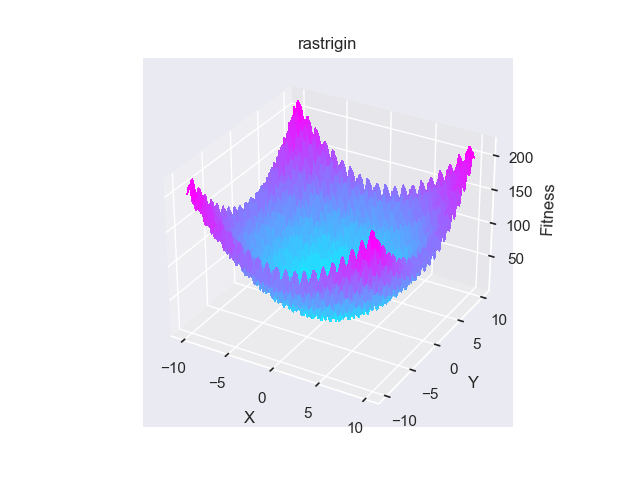
Bungert, L., Roith, T. and Wacker, P., 2024. Polarized consensus-based dynamics for optimization and sampling. Mathematical Programming, pp.1-31.
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x)[源代码]
**Scaled-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
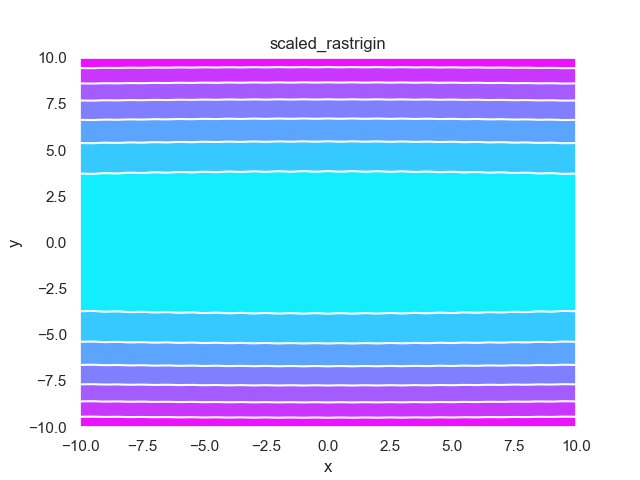
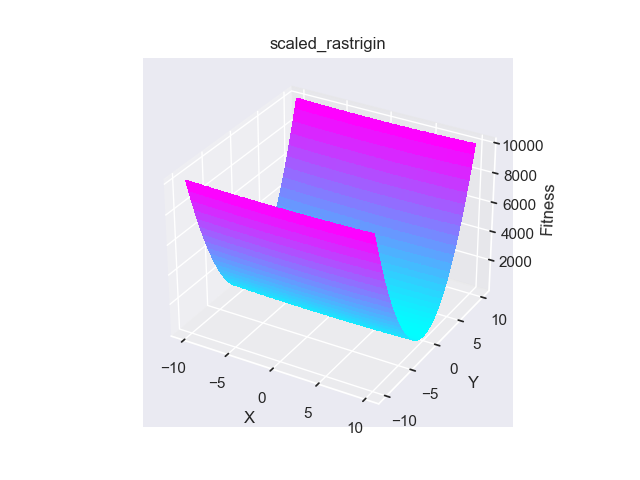
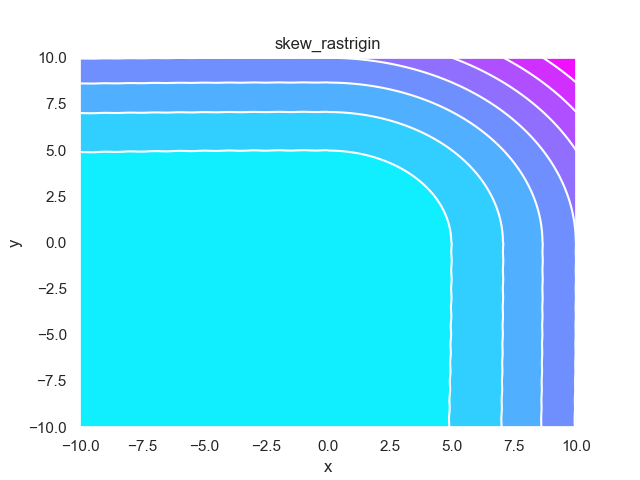
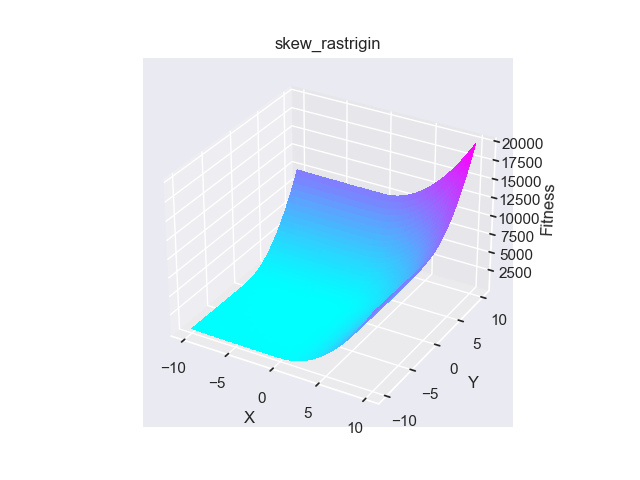
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.skew_rastrigin(x)[源代码]
**Skew-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
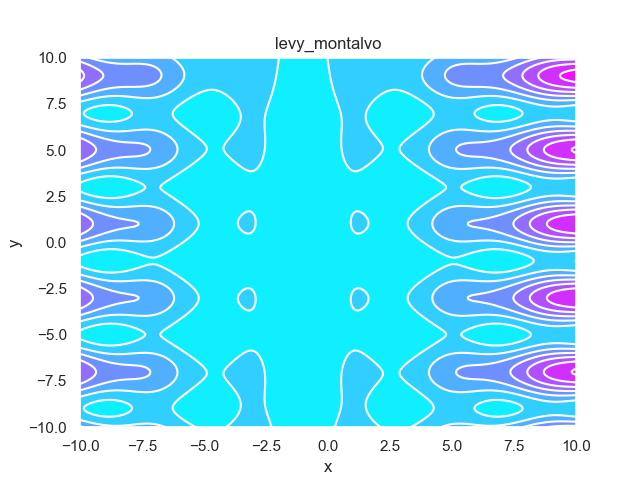
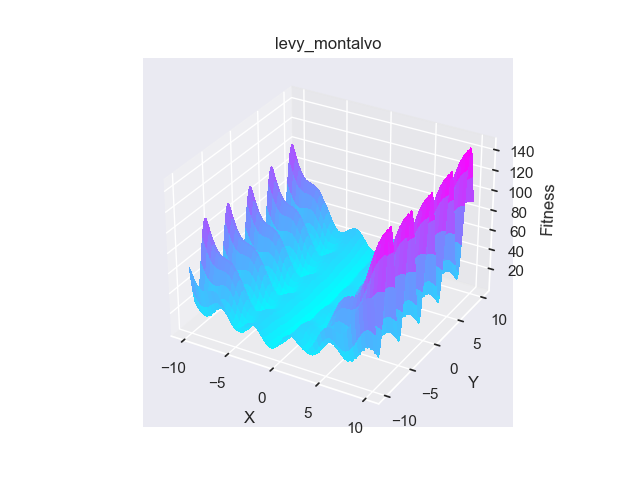
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.levy_montalvo(x)[源代码]
**Levy-Montalvo** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
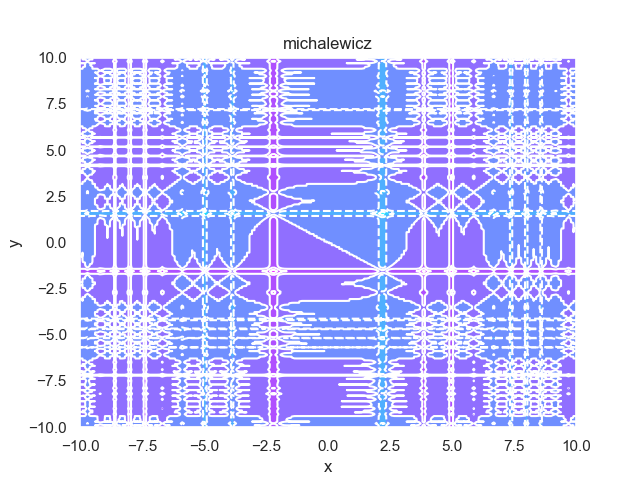
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.michalewicz(x)[源代码]
**Michalewicz** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.salomon(x)[源代码]
**Salomon** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
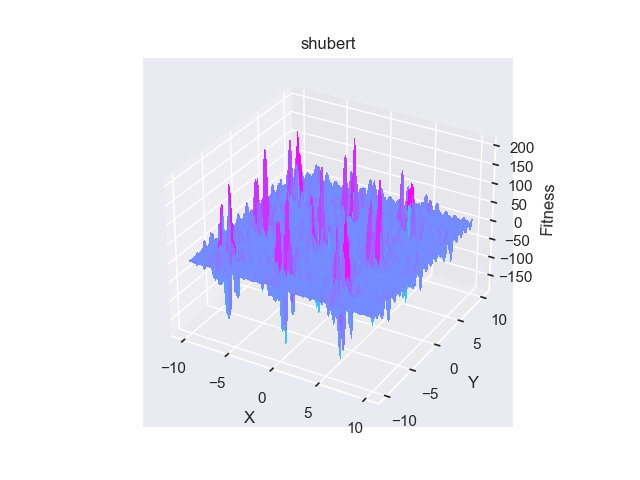
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.shubert(x)[源代码]
**Shubert** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
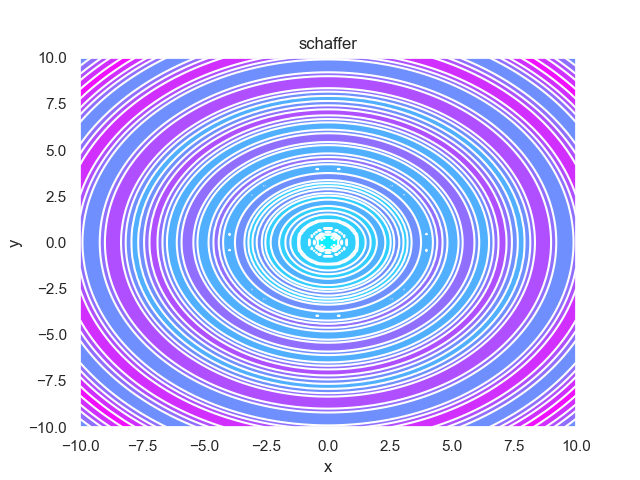
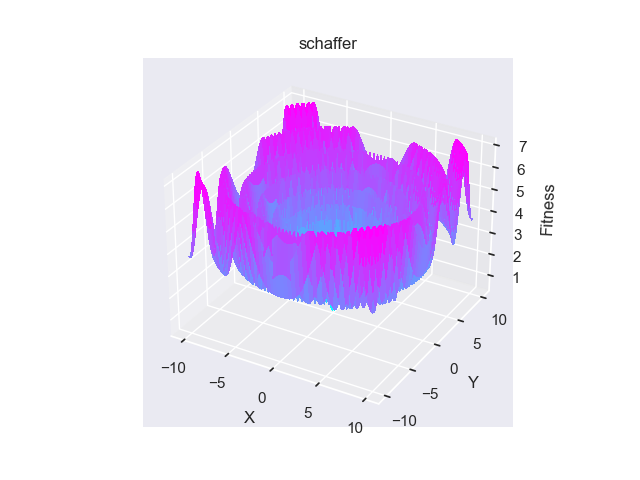
- pypop7.benchmarks.base_functions.schaffer(x)[源代码]
**Schaffer** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
平移/变换形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基本函数的**平移/变换**形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.generate_shift_vector(func, ndim, low, high, seed=None)[源代码]
- 生成一个维度为 ndim 的*随机*平移向量,在 low(包含)和 high(不包含)之间均匀采样。
在 low(包含)和 high(不包含)之间。
注意
生成的平移向量将自动以 *txt* 形式存储,**以供后续使用**。
- 参数:
func (str or func) – 函数名。
ndim (int) – 平移向量的维度数。
low (float or array_like) – 平移向量的下界。
high (float or array_like) – 平移向量的上界。
seed (int) – 用于随机数生成器 (RNG) 的标量种子。
- 返回:
shift_vector – 在 [low, high) 范围内均匀采样的大小为 ndim 的平移向量。
- 返回类型:
ndarray (数据类型为 np.float64)
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.load_shift_vector(func, x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
加载需要*预先*生成的平移向量。
注意
当为 None 时,平移向量应已通过 generate_shift_vector() **预先**生成并以 *txt* 格式存储。
- 参数:
func (func) – 函数名。
x (array_like) – 决策向量(也称为输入向量)。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
- 返回:
shift_vector – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
- 返回类型:
ndarray (数据类型为 np.float64)
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.sphere(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Sphere** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.cigar(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Cigar** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.discus(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Discus**(也称为 **Tablet**)测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.cigar_discus(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Cigar-Discus** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.ellipsoid(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Ellipsoid** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.different_powers(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Different-Powers** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel221(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel221** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.step(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Step** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel222(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel222** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.rosenbrock(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Rosenbrock** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.schwefel12(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel12** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.exponential(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Exponential** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.griewank(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Griewank** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
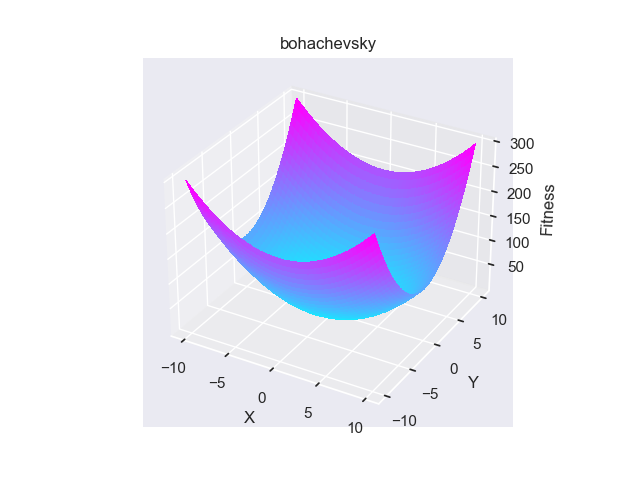
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.bohachevsky(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Bohachevsky** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.ackley(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Ackley** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Rastrigin** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Scaled-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.skew_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Skew-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.levy_montalvo(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Levy-Montalvo** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.michalewicz(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Michalewicz** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.shifted_functions.salomon(x, shift_vector=None)[源代码]
**Salomon** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 shift_vector 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_shift_vector() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (ndarray) – 与 x 大小相同的向量。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
旋转形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基本函数的**旋转**形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.generate_rotation_matrix(func, ndim, seed)[源代码]
生成一个维度为 [ndim * ndim] 的*随机*旋转矩阵,通过正态分布采样。
注意
生成的旋转矩阵将自动以 *txt* 格式存储,**以供后续使用**。
- 参数:
func (str or func) – 函数名。
ndim (int) – 旋转矩阵的维度数。
seed (int) – 用于随机数生成器 (RNG) 的标量种子。
- 返回:
rotation_matrix – 大小为 [ndim * ndim] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回类型:
ndarray
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.load_rotation_matrix(func, x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
加载需要预先生成的旋转矩阵。
注意
当为 None 时,旋转矩阵应已**预先**生成并以 *txt* 格式存储。
- 参数:
func (str or func) – 函数名。
x (array_like) – 决策向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
rotation_matrix – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回类型:
ndarray
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.sphere(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Sphere** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $sum_{i=1}^{n}x_i^2$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.cigar(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Cigar** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.discus(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Discus/Tablet** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.cigar_discus(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Cigar-Discus** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.ellipsoid(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Ellipsoid** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.different_powers(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Different-Powers** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel221(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel221** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.step(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Step** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel222(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel222** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.rosenbrock(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Rosenbrock** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.schwefel12(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel12** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.exponential(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Exponential** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.griewank(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Griewank** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.bohachevsky(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Bohachevsky** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.ackley(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Ackley** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.rastrigin(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Rastrigin** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Scaled-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.levy_montalvo(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Levy-Montalvo** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.michalewicz(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Michalewicz** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.rotated_functions.salomon(x, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Salomon** 测试函数。
注意
其 LaTeX 公式为 $$。如果其参数 rotation_matrix 为 None,请预先使用函数 generate_rotation_matrix() 生成它(以 *txt* 格式存储)。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 一个在每个维度上都与 x 大小相同的矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
旋转-平移形式
接下来,我们将介绍上述基本函数的**旋转-平移**形式,如下所示:
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.load_shift_and_rotation(func, x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
加载需要**预先**生成的平移向量和旋转矩阵。
注意
当为 None 时,平移向量应已**预先**生成并以 *txt* 格式存储。当为 None 时,旋转矩阵应已**预先**生成并以 *txt* 格式存储。
- 参数:
func (str or func) – 函数名。
x (array_like) – 决策向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
shift_vector (ndarray (数据类型为 np.float64)) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.sphere(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Sphere** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.cigar(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Cigar** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.discus(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Discus** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.cigar_discus(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Cigar-Discus** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.ellipsoid(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Ellipsoid** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.different_powers(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Different-Power** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel221(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel221** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.step(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Step** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel222(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel222** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.rosenbrock(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Rosenbrock** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.schwefel12(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Schwefel12** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.exponential(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Exponential** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.griewank(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Griewank** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.bohachevsky(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Bohachevsky** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.ackley(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Ackley** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.scaled_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Scaled-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.skew_rastrigin(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Skew-Rastrigin** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.levy_montalvo(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Levy-Montalvo** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.michalewicz(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Michalewicz** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
- pypop7.benchmarks.continuous_functions.salomon(x, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None)[源代码]
**Salomon** 测试函数。
- 参数:
x (ndarray) – 输入向量。
shift_vector (array_like) – 与 x 大小相同的平移向量。
rotation_matrix (ndarray) – 大小为 [len(x) * len(x)] 的旋转矩阵。
- 返回:
y – 标量适应度值。
- 返回类型:
float
大规模黑盒优化 (LBO) 基准测试
这里我们为大规模黑盒优化 (LBO) 提供了两种不同的基准测试案例(局部搜索与全局搜索)。
来自数据科学的黑盒分类
这里我们提供了一系列来自数据科学黑盒分类的测试函数。
基于 NeverGrad 的光子学模型基准测试
有关光子学模型的介绍,请参阅 NeverGrad。
基于 Gymnasium 的控制器基准测试
有关介绍,请参阅 Gymnasium(来自 Farama Foundation)。
来自 PyGMO 的 Lennard-Jones 团簇优化
有关这个来自 PyGMO 的 444 维 Lennard-Jones 团簇优化问题的介绍,请参阅 pagmo2(来自欧洲空间局)。
测试类和数据
下面,我们将为基准测试函数提供一组测试类和测试数据。由于这些类和数据仅用于测试目的,最终用户可以安全地跳过本节。
- class pypop7.benchmarks.cases.Cases(is_shifted=False, is_rotated=False)[源代码]
通过抽样测试基准函数的正确性(测试用例)。
- check_origin(func, n_samples=7)[源代码]
通过随机抽样检查函数值为零的原点(测试用例)。
- 参数:
func – 基准函数, func。
n_samples – 样本数量, int。
- 返回:
如果所有在测试用例上计算的函数值均为零,则为 True,否则为 False;bool。
- compare(func, ndim, y_true, shift_vector=None, rotation_matrix=None, atol=0.001)[源代码]
将真实函数值与所用基准函数返回的值进行比较。
- 参数:
func – 基准函数, func。
ndim – 维度数量(仅在 [1, 7] 范围内),int。
y_true – ndarray,其中每个元素是相应测试用例的真实函数值。
shift_vector – 平移向量, ndarray。
rotation_matrix – 旋转矩阵, ndarray。
atol – 绝对容差参数, float。
- 返回:
如果在测试用例上计算的所有函数值都与 y_true 匹配,则为 True;否则为 False。